Alexander Safonov – M.Sc. IT (Master of Science in Information Technology), Head of the Internet project in the field of Software Development & Digital Marketing (Washington DC, USA).
Artamonova Elena – PhD (Tech. Sci.), member of the International Academy of Information Technologies (IAIT), Head of the Internet project in the field of information security (Minsk, Belarus).
Abstract. In the article, the authors examine the main trends in the development of the IT sector during Industry 4.0. They highlight the basic technologies of the fourth industrial revolution. The authors make forecasts on the development of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), additive technologies, DevOps, virtual data centers, etc.
The article says how digital transformation is changing areas such as jurisprudence and public administration and introduces the following concepts: “LegalTech” and “e-government”. Information technologies are the basic technological package for a post-industrial society. All spheres of human activity work on the basis of IT, even education and art.
This article outlines how information security will evolve in Industry 4.0. The authors, along with positive trends in the development of IT, give forecasts on negative trends, such as: the danger of neo-feudalism, total control by states and corporations, deployment of tracking and control systems for citizens, deterioration of the quality of Internet services, etc.
Keywords: Industry 4.0., electronic government, Internet of Things, cloud computing, blockchain, cryptocurrencies, smart contract, digital art, LegalTech, information security, distance education.
Introduction
The beginning of the 21st century is the stage of the post-industrial transition, which came in the form of the fourth industrial revolution (Industry 4.0). According to many researchers, this is the transition to the sixth technological mode. These processes take place in the form of digital transformation (DT) and the formation of IT as the basic technological package of the economy. Information Technology is becoming the driver of the development of society. [Pereslegin S. B., 2015, pp. 207-224].
The post-industrial transition is a difficult process that can be painful for the economies of many states and society. There is also always the danger of a “phase disaster” and the beginning of a new “dark ages” (or “neo-feudalism”).
On the other hand, the rapid development of technologies that will significantly outpace the existing social relations may lead to a technological singularity. In our opinion, both options do not bring anything good to society. Therefore, the process of post-industrial transition should take place smoothly in the form of digital transformation (DT), during one there will be a gradual abandonment of outdated technologies, the maintenance of which costs enterprises too much. DT brings next changes in production culture: the use of the Internet of Things (IoT) , artificial intelligence (AI) , machine learning , blockchain , microservice architecture , etc. [Artamonov V А., Artamonova Е.V., 2019, p. 25]
The transition will be tough for many social groups, especially since it will take place at an accelerated pace against the backdrop of the coronavirus pandemic and the global financial crisis. However, there are also such groups of the population that will benefit significantly with the advent of a post-industrial society.
In this era, the IT sector is becoming an important one in the economies of many countries. Moreover, both old and completely new industries will be built on its basis. In our opinion, IT specialists and other citizens want to know which trends in IT will prevail in the near future.
Of course, forecasting the future is a thankless task. Many forecasts may not come true, but completely new, as yet unknown technologies will “shoot out”. But some trends can be seen already now, in the era of transition to the sixth technological order.
In our article, we will note those areas that will be basic for Industry 4.0., and will have a significant impact on the development of the economy, the social sphere and the public administration system.
[1] The Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0.) — conceptualizes rapid change in technology, industries, and societal patterns and processes in the 21st century due to increasing interconnectivity and smart automation. A part of this phase of industrial change is the joining of technologies like artificial intelligence, gene editing, and advanced robotics that blur the lines between the physical, digital, and biological worlds.
Basic technologies of Industry 4.0
According to futurologists, the basic technologies for the sixth technological mode will be: artificial intelligence, robotics, additive technologies , photonics , augmented and virtual reality, blockchain, cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, competent nature management, humanitarian technologies (reflexive governance , probabilistic models, etc.) . [Pereslegin S.B., Technologies…, 2020]
In this article, we will only touch on those technologies that are related to IT. In addition, we would like to note the importance of the following areas: remote work, e-learning, LegalTech, new generation of EDF , virtual data centers, IoT, etc.
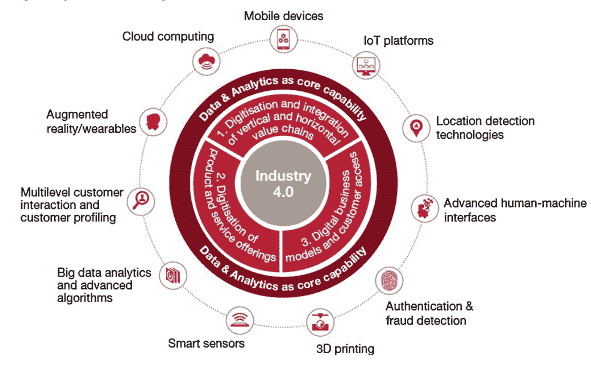
Industry 4.0
Fig.1 Industry 4.0. The role of Information Technology. Source: Bukht, Rumana. Defining, Conceptualising, and Measuring the Digital Economy. International Organisations Research Journal.
[1] Reflexive governance, as a new mode of governance, is viewed as organizing a response to the risks by replacing traditional, hierarchical, and deterministic governance approaches with more reflexive, flexible, and interactive ones, which draw on diverse knowledge systems.
[2] Humanitarian technologies (HT) are a set of technologies for influencing an individual or a group of people. They are also often referred to as “soft” influence technologies. Humanitarian technologies are technologies of a strategic nature that are aimed at solving problems in the long term. Ones are exclusive, they are developed for a specific issue block or project.
[3] Remote work is a working style that allows professionals to work outside a traditional office environment. It is based on the concept that work does not need to be done in a specific place to be executed successfully.
[4] Distance education, also known as distance learning, is the education of students who may not always be physically present at a school. Traditionally, this usually involved correspondence courses wherein the student corresponded with the school via mail. Today, it often involves online education. A distance learning program can be complete distance learning, or a combination of distance learning and traditional classroom instruction.
[5] Legal technology, also known as Legal Tech, refers to the use of technology and software to provide legal services and support the legal industry. Legal Tech companies are often startups founded with the purpose of disrupting the traditionally conservative legal market.
[6] Electronic document flow (EDF) is about moving documents into paperless form where electronic document signed by digital signature is fully legally binding, doesn’t require hard copy’ original at all and accepted by authorities as compliant.
[7] A virtual data center offers the capabilities of a traditional data center, but uses cloud-based resources instead of physical resources. It provides an organization with the ability to deploy additional infrastructure resources in need without acquiring, deploying, configuring, and maintaining physical appliances.
Development of robotics and artificial intelligence systems
Nowadays, we can observe the introduction of robotic systems. For example, these are drones, self-driving cars, robots for the delivery of goods, unmanned production, etc.
The goal of the sixth technological order is to build a unified robotic environment based on unmanned production. However, this fact does not mean that there will be no place for man in this new production system.
Let’s see how self-driving cars are tested. For example, accidents involving self-driving cars have been recorded, that’s why a mandatory condition is being put forward in the USA: “there must be a person in the driver’s seat who will be able to take control in case of an emergency”. The reason for putting forward such strict requirements is the inability of AI systems to make morally sound decisions, for example, in the event of an accident on the road and the likelihood of death of people. An experienced human driver can quickly make such complex decisions on the road, as a result of the ability to operate the first and second signaling systems. Also, a person can quickly make decisions based on moral and ethical principles. This ability is not yet available to AI systems and robots. It’s obvious, at the first stage, it is advisable to introduce collaborative robots (cobots). In emergency situations, the operators of such systems (people) will make the right decisions based on their experience and intuition, as well as their professional skills.
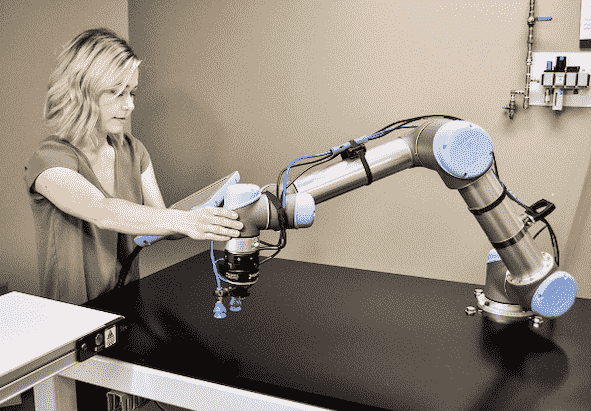
Fig.2
Collaborative robot (cobot). Source: Web-site Technored // URL: https://technored.ru/upload/iblock/8a4/8a4cd0687599047c9211f5c570a7b7ba.jpeg
However, in addition to industry and logistics, AI systems will be massively introduced into the intellectual fields of human activity. It is worth mentioning the following areas of IT: machine learning (ML), neural networks, “big data”, etc. Today, systems for machine translation of foreign texts are widely used. New systems that write texts themselves instead of journalists and copywriters have been developed and tested. IBM Watson is a supercomputer of IBM equipped with an artificial intelligence system. IBM Watson is an example of automation of management activities. A large class of problems are solved with the help of such a system — from research in the field of oncology to management decision-making at the level of large corporations.
Saying objectively that such a massive replacement of people in working, intellectual and managerial positions by robots and AI systems can lead to mass unemployment, inequality and poverty for millions of people. That’s why this negative trend must be stopped in any way with the help of humanitarian technologies. The “transitional period” to the sixth technological order will be especially difficult.
What can be proposed to reduce the impact of the negative social consequences of robotization on humans? This is the introduction of a universal basic income (UBI), mass retraining in new post-industrial specialties and a fair distribution of profits received from robotic production.
[1] A self-driving car, also known as an autonomous vehicle (AV), driverless car, or robotic car (robocar), is a car incorporating vehicular automation, that is a ground vehicle, that is capable of sensing its environment and moving safely with little or no human input.
[2] The First Signal System is the activity of the brain when specific stimuli act on the sensory organs. The first signal system includes: unconditioned reflexes and conditioned reflexes. The Second Signal System is the activity of the brain under the action of verbal stimuli.
[3] A cobot, or collaborative robot, is a robot intended for direct human robot interaction within a shared space, or where humans and robots are in proximity. Cobot applications contrast with traditional industrial robot applications in which robots are isolated from human contact.
[4] A neural network is a network or circuit of biological neurons, or in a modern sense, an artificial neural network, composed of artificial neurons or nodes. Thus, a neural network is either a biological neural network, made up of biological neurons, or an artificial neural network, for solving artificial intelligence (AI) problems.
Additive technologies
3D printing technologies have been widely used in production for several years now. According to experts, the market for additive technologies will grow to $21 billion by 2025.
The structure of the market for the use of additive technologies:
• the automotive industry – 20%;
• architecture – 4%;
• the aviation and aerospace industry – 15%;
• industry – 12%;
• consumer electronics – 28%;
• the medicine – 16%;
• other industries – 32%. [Frost & Sullivan…, 2018]
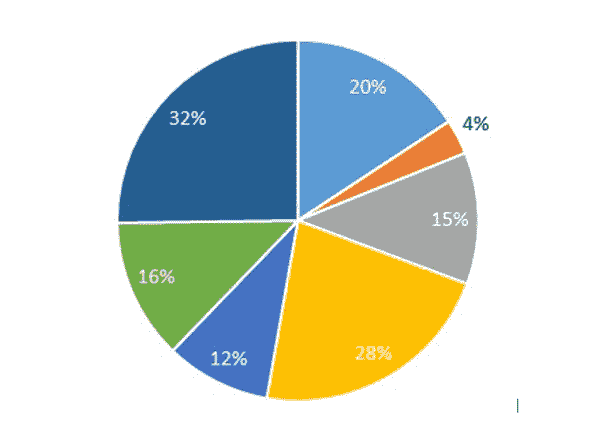
Fig.3
Additive technologies market, development forecast for 2025.
Source: Frost & Sullivan
The main trends in the 3D printing industry that have appeared this year:
1) The impact of the coronavirus pandemic has given an additional boost to the development of the industry.
2) 3D printing is considered a true industrial technology.
3) 3D printing software is becoming an urgent necessity for many enterprises. The characteristics of this software are improving.
4) New materials for 3D printing (granules, powder materials, graphite fiber, etc.) open up new areas of application for this technology.
5) Different industries use additive technologies in completely different ways.
6) In the future, leasing of 3D printers will be widespread.
7) The production of 3D printers will be developed, allowing you to create large-sized products with high accuracy, which will find their application in construction or mechanical engineering.
8) Graphene, a material promising for nanotechnology, will be used for the production of batteries and metal conductors. [Popadyuk S., 2021]
Virtual, augmented and mixed reality
There are several types of technologies that complement or change our reality or create an “artificial reality”. These are augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR) .
What is the difference between these technologies for the average user? Virtual reality constructs a new artificial world, and augmented reality only introduces some artificial elements into the perception of the real world. The main feature of mixed reality (MR) is the fact that virtual content is not just added to the real environment, as in AR, the user has a direct interaction with virtual content. Such mixed reality is a kind of augmented reality, but more interactive and captivating for the user.
[Konovalsky A., 2019]
Below we outline the areas in which VR, AR and MR will find applications in the near future.
Areas of application of virtual reality (VR):
• education and learning management systems;
• real estate industry;
• marketing and advertising;
• engineering and design;
• medicine and healthcare.
Areas of application of augmented reality (AR):
• training for new professions;
• advertising industry;
• manufacturing;
• retail and e-commerce;
• navigation apps;
• maintenance and repair.
Areas of application of mixed reality (MR):
• area of communications;
• production;
• educational programs;
• entertainment (games, interactive films, etc.). [Konovalsky A., 2019]
Let’s tell you on a practical example how some developers are already adding elements of augmented and even virtual reality to their applications. For example, a mobile app wARna has been developed at the Malaysian University of Technology (UTM) that teaches young children how to draw remotely using AR. First, you need to purchase a coloring book, colored pencils and install this mobile application on your smartphone. Then you need to draw an image with pencils in a book, scan it in a mobile application, and we will get a three-dimensional model of our drawing, using the same color scheme as in the coloring book.
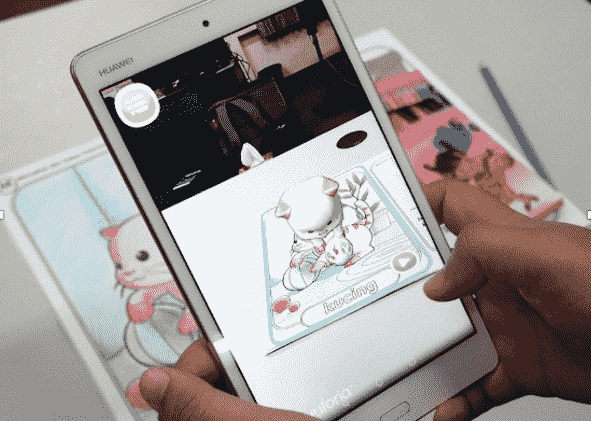

Fig.4
Fig.4 How the wARna app works using AR. Source: Google Play
Blockchain, cryptocurrencies and smart contracts
The topic of cryptocurrencies and blockchain suddenly became popular more than a decade ago. Judging by citizens’ opinion, distributed registries (blockchains) are primarily associated with bitcoin mining and operations on crypto-exchanges. However, the scope of blockchain technology is very diverse: fintech and cryptocurrency exchanges, LegalTech and public administration, education, cybersecurity, blockchain in corporate projects (private cryptocurrencies), non-fungible tokens (NFTs) etc.
For example, in the near future, large corporate or intra-industry projects will increasingly use private cryptocurrencies (tokens) for internal payments. This is convenient for large construction projects or in the field of commercial real estate sales.
What is the issue of a private cryptocurrency? Developers create their own cryptographic code using a ready-made token based on Ethereum. Then such a code is edited and adjusted to its own conditions, then the release of its own “coin” begins. [Blockchain, private cryptocurrencies…, 2020].
It’s obvious, it will be easier and more reliable to fix various agreements between counterparties using smart contracts, which are written in special programming languages (for example, Solidity). From a mathematical point of view, a “smart contract” is an “if… then…” algorithm. A smart contract is executed in a special computer environment, the participation of the parties is not necessary. Ethereum, IBM Bluemix are widely used platforms for implementing blockchain projects. [What are smart contracts…, 2021].
In the future, ordinary specialists (managers, lawyers, etc.) will be able to write smart contracts without the help of programmers. Most likely, it will be possible to implement various types of contracts based on smart contracts (for example, multi-stage process of delivery products using complex logistics, etc.) with the introduction of IoT technologies.
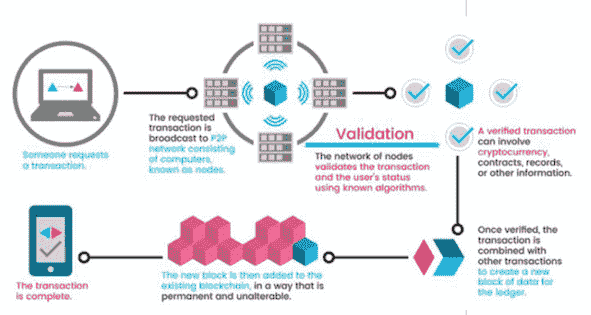
Fig.5
In the following sections of the article, we will focus in more detail on the use of blockchain and smart contracts in the legal field, in cybersecurity, in public administration, and other areas.
Digital transformation
As it’s well known the transition period in the process of Industry 4.0. will be accompanied by a process of digital transformation.
Digital transformation is the integration processes of digital technologies in all areas of business and aspects of human society life. These transformations require fundamental changes in manufacturing processes, culture, industrial relations, business, product and service development principles. Digital transformation cannot be considered as a one-time product of IT companies or a consulting service. This is a long and consistent process that modern enterprises must go through to enter the sixth technological order. The management of the enterprise must:
1) write a strategic plan in which the business needs of the company will be fixed;
2) organize training of employees in the skills of working with IT products and services;
3) abandon most of the outdated technologies;
4) deploy a modern infrastructure based on intelligent technologies, such as virtual data centers, IoT, distributed registries, DevOps and others. [Artamonov V. A., Artamonova E. V., 2020, p. 28]
E-Government, Jurisprudence and IT
An indispensable attribute of a post-industrial society is e-government. Electronic government includes the methods of obtaining information and providing a specific set of public services to citizens, businesses, other branches of government and civil servants, in which personal contact between the state and the citizen is minimized.
If we consider e-government from an IT point of view, then it is presented in the form of well-organized electronic document management systems (EDMS) and fully automated public administration systems. As a result, the quality of state services is increased, and the contact of a citizen with officials is minimized.
E-government is an important element of the digital economy, which solves the following problems:
• optimizes the process of providing state services to the public and business;
• supports self-service processes of citizens via the Internet;
• ensures the growth of technical education and qualifications of ordinary citizens;
• eliminates the role of the geographical location of a particular citizen. [Manshin G.G., 2014, p. 192]
As a result of the introduction of electronic public administration systems, the quality of work of all state and municipal services improves, less costly and more efficient administration is carried out, all branches of power and the democratic process are improved, and the responsibility of power to the people is increased. [Artamonov V. A., Artamonova E.V., 2020, p. 28].
An integral process of democracy is fair and transparent elections, which are planned to be held by electronic voting in the near future. Blockchain-based voting systems are already gaining popularity, which should ensure transparency and security of voting, and exclude changes in information on ballots. For example, such a system was developed and implemented by DIT of Moscow with the participation of Kaspersky Lab. However, these systems are still vulnerable in terms of information security and have problems in terms of vulnerabilities and threats, which are still holding back the spread of electronic voting systems. [Sunoo Park… 2021.]
LegalTech and new EDMS
LegalTech (LawTech) are new areas of electronic business that serve as information technology services for providing legal services to citizens using information and communication technologies. The key factor of LegalTech is a special toolkit that makes it possible to perform legal procedures by non-specialists. Thus, an ordinary citizen can analyze and prepare legal documents on his own using special software. [Keppenne R., 2016, p.48]
Let us briefly consider on what basis LegalTech systems can be built. First, this is a new generation of EDMS, which is already being developed and will soon be widely used. Such EDMS are built on the basis of semantic and ontological methods . The main principle of next generation EDMS is the transition from human-readable to processed by software descriptions of electronic documents. That is, documents will be developed not only for human reading, but they are also structured in such a way that machines can read them. Special markup languages are used for this. [Artamonova, E.V., 2020, p. 324]
At the next stage, blockchain technology is connected. For example, real estate transactions and other simple legal transactions are already being transferred today on the blockchain technology. Such agreements are carried out on the basis of smart contracts, where all the terms of the transaction will be written in the form of a special algorithm, timestamps will be affixed. Then an electronic document (or a record of the transaction) will be entered into the blockchain. [Artamonov V. A., Artamonova E.V., 2019, p. S.26].
Cloud computing and a new concept of data centers
Digital transformation is changing the essence of time-established IT services. Now we can observe how the concept of services of hosting providers and data centers is changing. Recently, in addition to traditional site hosting, colocation, etc. hosting companies began to offer completely new services: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS. Below, we will consider in more detail the advantages of these solutions.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a type of cloud solution that gives the right to use resources for computing, data storage, network connections on demand (with a certain fee). The advantage of this solution is that the user can deploy and scale IT solutions without investing in the process of purchasing and maintaining equipment.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a software development and deployment environment in the cloud with resources. In this environment, any applications are provided to the client, ranging from the simplest applications to advanced enterprise applications. The user purchases resources from a cloud service provider, pays as they are used. The main use of PaaS is to support the life cycle of a web application:
• developing and writing code;
• application testing by a team of testers;
• deploying the application in the cloud;
• application management;
• software updates.
The popularity of “software as a service” (SaaS) solutions is increasing. This is a model of providing client access to software via the Internet, using cloud solutions.
As we can see, all these three new models are united by the principle of “rent” (software, infrastructure, platforms). The user does not need to buy expensive equipment on full ownership, deploy and maintain complex platforms on their own, or constantly configure and update software by buying expensive licenses for it. All this work is done for him by the service provider, the so-called “virtual data center”, and the client pays him for the services upon their use. [As a hosting provider…, 2021]
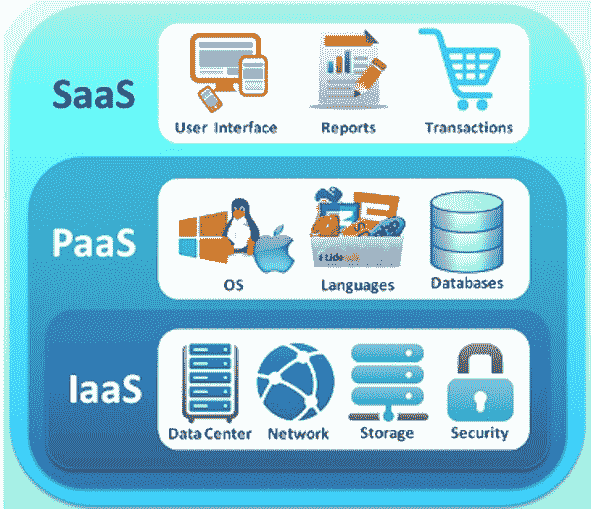
Fig.6
Source: Web-site Learn // URL: https://learn.trudmore.ru/assets/uploads/Cloud-Service-Models.png
How Cybersecurity will change
It’s clear the IT infrastructure of enterprises and corporations is becoming much more complicated in the era of digital transformation. These are corporate networks, including cloud computing , servers, virtual data centers, virtual environments, mobile devices, etc. On the other hand, modern cybercrime is no longer just a community of self-taught hackers, it is a developed shadow business, with well-established business processes and specialization. The cyber threat landscape is changing over time. New types of attacks and threats have appeared (for example, DDoS attacks , phishing , ransomware , etc.). Attacks are becoming more complex. Attackers often use a new type of attack against corporate systems — APT , so hackers can stay inside the perimeter of the corporate network for quite a long time. It should be noted that preventive (classic) protection methods cannot always help protect the company’s IT infrastructure. [Threats to information…, 2021].
The practice of information security (IS) specialists includes proactive (innovative) methods, which include, as well-known solutions, such as honeypots and honeynets , and more modern “Deception technologies” . Generally speaking, the principle of Deception technology is the following: the company’s IT infrastructure is deployed in the form of two layers: the first layer is the real infrastructure of the organization, and the second layer is the “illusive IT infrastructure”. [Evolution of methods…, 2020].
However, the process of digital transformation has its negative side. It consists in the emergence of new vectors of threats to information security. For example, we list the following negative factors:
— opacity of information security events;
— unreality of automation of all IS processes;
— problems with the integration of information security solutions;
— flexible scaling of software that can lead to new vulnerabilities;
— negative consequences of software updates.
In the conditions of instability which digital transformation brings and the emergence of new threats to information security, cyber resilience is of particular relevance.
Cyber resilience is a property of an IT system to achieve the goal of its functioning under the conditions of information and technical impacts of external or internal threats, in the presence of vulnerabilities, sometimes even with a pre-admissible degradation of its productivity. [Artamonov V. A., Artamonova E.V., 2021, p.12].
Undoubtedly, solutions based on blockchain technology come to cybersecurity. One such example in this area is the Certcoin project — an alternative, public and decentralized authentication scheme. [Petrenko S.A., Petrenko A.S., 2019, p.19]
IT in post-industrial education and organization of remote work
In the corporate and the SMB sectors it has been a clear trend the transition from the office to “remote”. We note the basic trends for the next few years:
1) Employers and staff prefer the remote work format in those areas where you can work without being in the office all the time (or organize a flexible work schedule).
2) On the one hand, there is a decrease in overhead costs for employers (for office rent and the purchase of expensive equipment). On the other hand, new cost items for “remote employees” appear (depreciation of their own computer equipment and gadgets, increased payments for electricity and other utility costs, the need to in additional rooms for working at home, etc.). These cost items are rarely fully compensated by employers.
3) A negative trend is possible towards cutting the “social package” for remote workers (payments to the pension fund, medical insurance, etc.) and shifting these costs to the workers themselves, i.e. partial transfer of the staff to “self-employed”, “freelancers” and “individual entrepreneurs”.
4) The skills of managing remote teams and organizing communications will be in demand. Special software for managing projects and tasks will be supplemented with new functionality (to ensure communication in remote teams and their effective control). Learning management systems (LSM) will also become popular.
5) Most likely, in the next few years, the demand for AR / MR / VR technologies and their use in remote work will increase, for example, for organizing “virtual offices”, negotiations, etc.
6) Agile project management (Agile, Scrum, Kanban, etc.) are becoming very popular. These methods are already being applied in other areas, not just in the IT field.
7) More and more employees are starting to work for global structures (multinational corporations, foreign companies, international freelance exchanges, etc.). This factor generates a demand for learning foreign languages, especially English. Despite the development of machine translation systems, they still do not fully meet the requirements for high quality of translated information.
8) The transition of many people into “self-employed”, “freelance”, etc. generates a demand for legal, medical, psychological and other information, because these categories of citizens will have to solve many social problems on their own. Thus, it is possible to predict the further development of LegalTech, telemedicine, etc. projects.
9) Cloud solutions will become more and more popular as they facilitate the organization of remote work of employees. In software development, the popularity of microservice application architecture and cloud computing will increase.
10) Transferring a critical mass of employees to remote work creates high risks and threats of cybersecurity that’s why knowledge in this area (Cybersecurity awareness) will become vital for ordinary Internet users. [Artamonova E.V., Artamonov V.A., 2021, p.65].
Distance education trend
Recently, distance education has been gaining popularity in the field of postgraduate education or corporate education. However, in the pandemic and quarantine conditions, schools, colleges and universities began to urgently transfer to remote learning.
At first, teachers used free messengers, video communication programs (such as Zoom), e-mail, etc. But there is a slow transition to more professional products and systems. [Artamonova, E.V., 2020, p. 324].
Let’s note a few basic trends in the field of post-industrial education:
1) The principle of “lifelong learning” is gaining popularity , which means the emergence of a new market for adult education. The first education received in youth no longer guarantees a job in this specialty for the entire working life.
2) The trend for distance education will only continue to develop in schools, colleges and universities, but not only in the field of corporate and postgraduate education.
3) The rapid change of technology leads to the fact that classical technical education in universities (according to the old programs) is no longer able to satisfy the demand of employers for IT specialists. Without any doubt, additional independent or corporate education will be an obligatory stage in the life of an IT specialist.
4) In areas strongly tied to new technologies, the transfer of knowledge and skills will occur from the younger to the older generation (i.e. not in the same way as in traditional societies). This is already noticeable in the IT sector. A huge role will be played, not just in knowledge and information that can be found on the Internet, but in professional skills and the ability to effectively search for information on the net. [Artamonova E.V., Artamonov V.A., 2021, p.65].
Negative trends in IT development
The rapid development of the IT sector during the period of digital transformation and the transition to the sixth technological mode carries both positive and negative factors. Let us note the main negative trends that have already been outlined and could be developed in the near future.
1.The spread of the “Social Credit System” . Nowadays, such a system has been deployed and is being tested in China. Chinese government structures use Big Data technologies and electronic systems of mass surveillance for evaluation of all their citizens in many ways. The government uses a carrot and stick policy. A person is assessed based on a lot of data (payment discipline, loyalty to the authorities, behavior in society and activity on the Internet, the circle of relatives and friends, etc.). Judging by this “rating”, a citizen either gets access to various benefits, or he/she is restricted from accessing them. For example, people with a low social rating are restricted from moving around the world and the country, in access to education and a good job, etc. So far, this system has been deployed only in China, but the authorities of some other countries are also eyeing it and trying to apply its individual fragments. [How does the Chinese…, 2018] From our point of view, the Social Credit System is a huge step towards “digital totalitarianism” and a negative experiment on society which has no place in a democratic post-industrial society.
2. A rollback to “neo-feudalism”. At the beginning of our article, we already warned about the danger of the onset of “neo-feudalism” or even a “phase disaster” as a result of the unsuccessful completion of Industry 4.0. How can such a “neo-feudal” society be characterized? It will include “new patricians” who own resources and means of production — these are billionaires, high-ranking officials and oligarchs. A small percentage of “service personnel” will be concentrated around them, who will also live well. On the other side of society, there will be a small percentage of well-educated, creative people who will work in the post-industrial field and also have a high standard of living. The bulk of the citizens will be poorly educated, poor and lead a primitive lifestyle in search of “bread and circuses”. This imbalance can be eliminated by modernizing the education system, reorienting it to develop the creative abilities of an increasing number of people, and teaching them new post-industrial specialties.
[Artamonova E.V., Artamonov V.A., 2021, p.65].
3. Total digital control of the state. Already, in many states there are noticeable “excesses” towards total control of the Internet and society with the help of electronic means of surveillance. Especially negative trends are the widespread installation of face recognition system in major cities, unrestricted use of biometrics (which is accompanied by a leak of personal data) , blocking resources on the Internet (for example, because of “dissent”), a targeted communication quality degradation (use of DPI technology , Internet shutdown , traffic shaping , QoS ), etc. [What to do… 2020]
4. Monopoly of digital platforms and transnational corporations . Recently, the market has been monopolized by such well-known companies as Google, Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Microsoft, etc. Digital giants have completely monopolized the sphere of social networks, search engines, proprietary software and other digital services. If at the initial stage, these corporations brought technical progress to citizens, now they bring users a lot of negativity. For example, the Google search engine may lower interesting small sites with valuable scientific information in the SERP. Facebook can “block” its users for a long time, assign (or delete) their copyrighted content based on the actions of its robot programs, the opinion of an unknown system administrator, or on the complaint of a “bot”. Moreover, users do not have effective mechanisms to fight monopolists. Although in the future, it is not excluded the creation of “digital resistance” against monopoly platforms and agencies that censor the Internet. For example, open source’ platforms are emerging that do not censor information posted by users (for example, Mastodon, Friendica, Peertube, etc.) or new commercial platforms (Medium, Substack, etc.) that do not seek to monopolize the market. However, the monopolists also “do not give up”. Facebook plans to build the Metaverse (Meta), where the user will be immersed in a completely virtual world using VR/AR technologies. Of course, the idea is very tempting. But there is also a negative forecast that all this may turn out to be just a “PR” or end in a dystopia. [Loginov N., 2021].
Conclusion
The trends in the development of the IT sector in the process of the formation of Industry 4.0 described in this paper lead us to the following conclusions:
— Information technologies, in the process of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, become the basic technological package of the post-industrial era.
— Based on the level of technology development today, it is possible to determine the IT development trends for the next few years. Forecasting the development of IT for long periods of time (50-100 years) is quite difficult, as new technologies that we do not yet know about can suddenly “shoot out” (for example, blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies in 2009). So, to speak the popular technologies used now can become forgotten and unnecessary to society (for example, mainframes, paging systems, etc.). As it’s well known the technology can be popular for a certain period of time, then become “temporarily forgotten”, and then be reborn at a new level (3D technologies, for example).
— Traditional areas of activity (education, law, election process, art, etc.) are being transformed on the basis of IT. New areas are emerging: LegalTech (LawTech), distance education and work, digital art, etc.
— The approach to developing IT products and applications is changing, the daily activities of developers include: microservice architecture, DevOps, cloud computing, “IT product or technology – as a service” (SaaS, IaaS, PaaS), virtual data centers. Cybersecurity is evolving to new level of concepts and solutions.
— Such services as “Internet of Things” (IoT), “smart home”, “smart city”, etc. will enter the life of people very soon.
— Production and business processes of companies are gradually changing in the course of digital transformation. A new way of producing various goods based on additive technologies is coming.
— The sphere of government of countries and regions includes such a concept as “electronic government”, public services are becoming more accessible and more convenient for the vast majority of citizens.
— At the same time, scientific and technological progress also has negative aspects, which we also described in this article.
[1] Facial recognition is a way of identifying or confirming an individual’s identity using their face. Facial recognition systems can be used to identify people in photos, videos, or in real-time. Facial recognition is a category of biometric security.
[2] Biometrics is the measurement and statistical analysis of people’s unique physical and behavioral characteristics. The technology is mainly used for identification and access control or for identifying individuals who are under surveillance. The basic premise of biometric authentication is that every person can be accurately identified by intrinsic physical or behavioral traits.
[3] Personal data is any information that relates to an identified or identifiable living individual. Different pieces of information, which are collected together, can lead to the identification of a particular person, and also constitute personal data.
[4] Deep packet inspection (DPI) is a type of data processing that inspects in detail the data being sent over a computer network, and may take actions such as alerting, blocking, re-routing, or logging it accordingly. Deep packet inspection is often used to baseline application behavior, analyze network usage, troubleshoot network performance, ensure that data is in the correct format, check for malicious code, eavesdropping, and internet censorship.
[5] An internet shutdown is an intentional disruption of internet or electronic communications, rendering them inaccessible or effectively unusable, for a specific population or within a location, typically to exert control over the flow of information.
[6] Traffic shaping (also known as packet shaping) is a bandwidth management technique that delays the flow of certain types of network packets in order to ensure network performance for higher priority applications. Traffic shaping essentially limits the amount of bandwidth that can be consumed by certain types of applications.
[7] Quality of service (QoS) is the use of mechanisms or technologies that work on a network to control traffic and ensure the performance of critical applications with limited network capacity. It enables organizations to adjust their overall network traffic by prioritizing specific high-performance applications.

